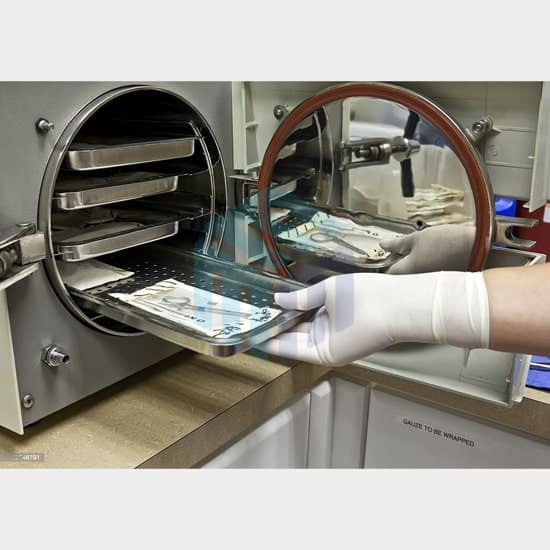
The medical industry utilizes various sterilization techniques to ensure the elimination of microorganisms and achieve a high level of cleanliness and safety for medical instruments, equipment, and supplies. Here are some common sterilization techniques employed in the medical industry:
- Steam sterilization (Autoclaving): Autoclaving is one of the most widely used and effective methods of sterilization. It utilizes saturated steam under pressure to kill microorganisms. The high temperature (typically 121°C to 134°C) and pressure (15 to 30 psi) generated inside an autoclave chamber ensure efficient sterilization. It is suitable for heat-resistant materials such as metal instruments, glassware, and certain plastics.
- Ethylene Oxide (ETO) Sterilization: Ethylene oxide is a gas commonly used for sterilization when heat and moisture-sensitive items need to be sterilized. ETO sterilization is performed in special chambers that allow for controlled exposure to the gas. It is effective against a wide range of microorganisms, but it requires proper aeration time to remove residual gas. ETO sterilization is commonly used for plastic devices, electronic components, and delicate instruments.
- Dry Heat Sterilization: Dry heat sterilization involves the use of high temperature to achieve sterilization. It is particularly suitable for materials that may be damaged by moisture or steam. This method usually requires higher temperatures and longer exposure times compared to autoclaving. Dry heat sterilization is commonly used for items such as glassware, metal instruments, and powders.
- Chemical Sterilization: Chemical sterilization involves the use of liquid or gas chemicals to eliminate microorganisms. One common method is the use of hydrogen peroxide gas plasma sterilization. It involves exposing the items to a low-temperature plasma generated by hydrogen peroxide gas, which effectively kills microorganisms. Chemical sterilization is often used for heat and moisture-sensitive items, such as certain plastics and electronic components.
- Radiation Sterilization: Radiation sterilization utilizes ionizing radiation, such as gamma rays or electron beams, to kill microorganisms. The radiation damages the DNA of the microorganisms, rendering them incapable of reproduction. This method is commonly used for single-use medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and some laboratory supplies. However, it requires specialized equipment and processes.
- Filtration: Filtration is a sterilization method used for heat-sensitive liquids or gases. It involves passing the substance through a membrane or filter with pores small enough to trap microorganisms. Filtration is commonly used for sterilizing certain pharmaceuticals, intravenous fluids, and air in cleanrooms.
Each sterilization technique has its advantages, limitations, and suitability for specific materials and applications. The choice of sterilization method depends on factors such as the type of items to be sterilized, their compatibility with the sterilization process, and the desired level of sterility. It’s important to follow established guidelines, manufacturer’s instructions, and regulatory requirements when implementing any sterilization technique to ensure proper and effective sterilization. M-Kube Enterprise is an Australian company catering customized laboratory products, laboratory consumables and laboratory solutions in Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Malaysia, South Korea, India, Dubai, Philippines, Indonesia and Vietnam.